
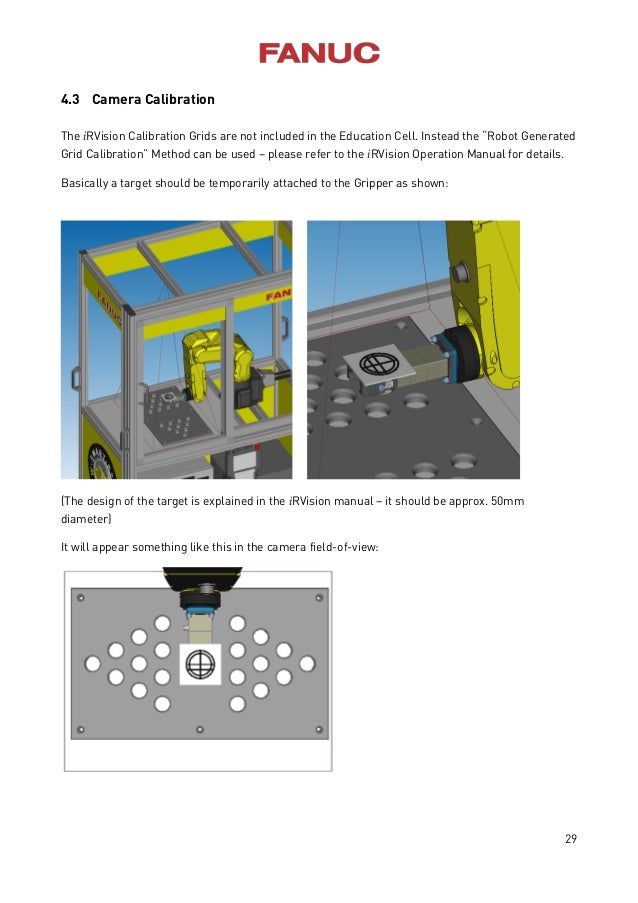
FANUC IR VISION CALIBRATION MANUAL
“Until recently, it was not easy to off-line program a robot without having to perform extensive manual touch-up of the programs on the production floor. Even vision programming can be accomplished offline. Robot programs can then be generated automatically from these selected features. Using ROBOGUIDE’s built-in utilities, part features can be selected from 3-D CAD data of the part. ROBOGUIDE allows users to import 3-D representations of robots, parts and system peripherals to create realistic “virtual” workcells.
FANUC IR VISION CALIBRATION OFFLINE
For example, an advanced deburring process can begin offline with products such as FANUC Robotics’ ROBOGUIDE PC-based simulation software.
High accuracy is also critical in data driven applications – those developed using offline programming methods. “The introduction of robotic accuracy into the manufacturing process guarantees that this replacement is smooth, does not interrupt the manufacturing process, is cost-effective and highly accurate,” said a company spokesperson. Eliminating these adjustments by machining or assembling precisely formed parts allows for predictable and timely part replacement, reducing costs and downtime and allowing for parts to be interchanged repeatedly without any interruption in production. Reducing fastener tolerances not only improves the reproducibility of an assembled component, it also allows for a reduction in overall structure weight due to reduced fastener size and weight. Inconsistent and inaccurately machined or assembled replacement parts might traditionally have meant time lost due to trimming, deburring or other adjustments. Recently, for example, manufacturers are demanding high wear parts that require frequent maintenance and replacement be replaced seamlessly with identically manufactured parts. Some processes will only require positional accuracy while others require path accuracy, and some applications will require both. The level of accuracy should be defined according to the process requirements. Different levels of accuracy require different solutions the higher the accuracy required the more factors that must be considered, adding to the cost and complexity of the solution. Because there are many factors that influence robot accuracy, it is important to define the accuracy requirements for the system. The standard is set by the positional requirement for drilling of fastener holes which has been taken as a key target application for robotics in aerospace manufacturing. Typical tolerances for airframe assembly fastening were in the + 0.030″ range. Critical aerospace manufacturing techniques such as fastening and drilling were historically not held to tight tolerances. In the past, robotic accuracy has not been published or developed to a level of maturity acceptable to standard production processes. Where accuracy is concerned, robots have traditionally relied on repeatability.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
